Trading, A Way of Life
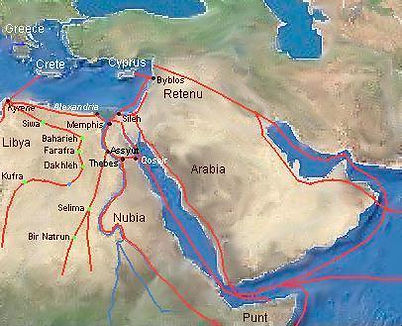
Trade in Ancient Egypt was a way of life. It helped to boost the economy in a way we could have never imagined. Trading gave Ancient Egyptian’s new goods they never would have dreamed of before. The goods they received helped them to survive in their everyday life, they were practical as well as luxurious. They traded with many countries around them; they used trades routes on land and on water. Their main export was grains, cloth, parchment and dried fish.
Some of the most important items of trade came from South West Asia This trade rout was crucial because it helped Ancient Egyptian’s to settle down and form communities. Ancient Egyptians were introduced to crops that were better for the winter rainfall such as emmer and barley. They were also introduced to domesticated animals such as sheep, cattle, pigs and goats. (Butzler, p.8). The trade to South West Asia happened by water and land; through the Red Sea and through the Sinai Peninsula. They entered through the western dessert, Sudan or steppes (Butzer, p. 9).
Animals and animal byproducts were a big part of the trading that the Ancient Egyptian’s conducted. Camels were introduced to the Ancient Egyptians by the Persians. The trade of camels helped the Ancient Egyptians to travel greater distances without having to worry about giving the camels water (Wilkinson, 2010, p.427). This helped to increase the economy because it allowed the Ancient Egyptian’s to trade in places that were farther away. Horses were eventually brought into to the equation through trading (Anonymous, 2000, website, Ancient Egyptian overseas trade).
Kebny was also an important trade partner with Ancient Egypt. It supplied Ancient Egyptian’s with important material: cedar. Cedar was very important to the Ancient Egyptian’s because they did not have an abundance of wood. The cedar wood was used to build ships. (Wilkinson, 2010, p.52). Wood was also important because it was used to build many other structures; it was used to build houses, and furniture as well. They also obtained wood from Babylon and Lebanon. They also imported other types of wood such as ebony, a variety of hardwood and even fragment woods that came from Africa. (Anonymous, 2000, website, Ancient Egyptian overseas trade).
Ancient Egypt also traded for precious metals. They did have some gold, and very little silver, iron and copper. They did not have enough to please the country so they had to trade for more. They were able to mine for gold and copper in Nubia and Sinai. They also traded for copper from Cyprus (Anonymous, 2000, website, Ancient Egyptian overseas trade). The imported metal was used for jewelry, tools and weapons.
In the end trade was important because it helped the economy to grow. They were able to build more, and explore more. These goods helped the economy because they were able to settle down, increase their wealth and sustain their lives through crops from other countries. By the economy getting stronger through trade, the military also got stronger because of the import of weapons from Crete and the Middle East (Strouhal, 1992, p.199). Trade was a huge part of the economy and it was a way of life.
Bibliography:
"Ancient Egyptian Overseas Trade." Overseas Trade during the Pharaonic Period. N.p., 2000. Web. 01 Nov. 2014.
Butzer, Karl W., “ Early Hydrolic Civilization in Egypt”. Chicago, 1976, print
Strouhal, Eugen. Life of the Ancient Egyptians. London, 1992, print
Wilkinson, toby. “The Rise and Fall of Ancient Egypt”. New York, 2010, print.